Top Trends in Cybersecurity in 2024
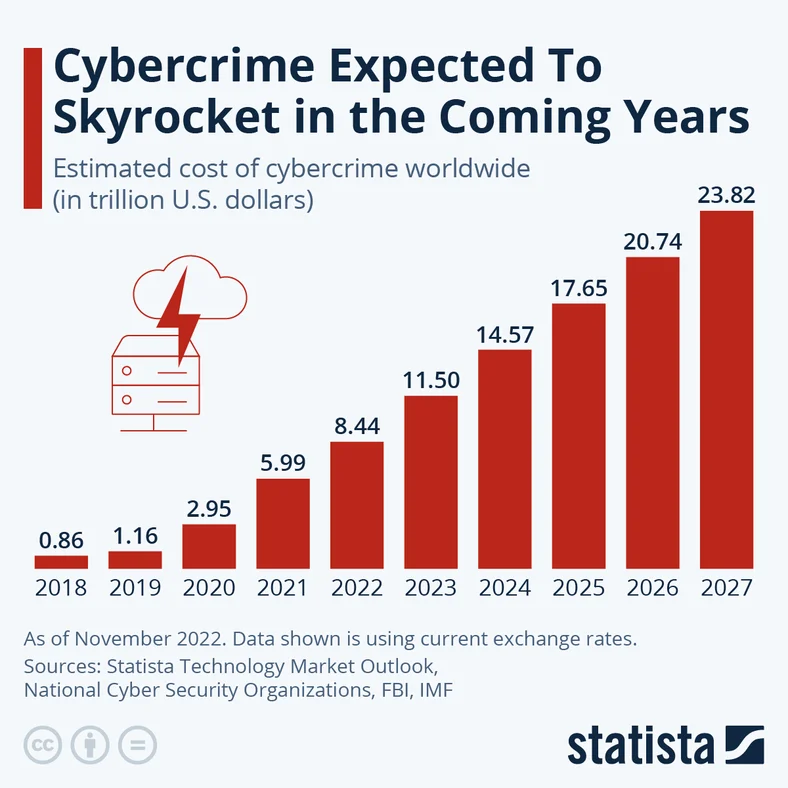
According to eSentire’s 2023 Official Cybercrime Report, “the global annual cost of cybercrime is predicted to reach $9.5 trillion USD in 2024.” Cybercrime is predicted to increase exponentially over the next several years. As cyber threats continue to increase in frequency and sophistication, focus is being placed on the critical need for organizations to emphasize the development of a strong cybersecurity stance.
How do you develop a strong cybersecurity stance?
Developing a strong cybersecurity stance involves a multi-layered approach that includes several steps. When creating a strong stance, organizations identify risks, implement multiple defenses like firewalls and encryption, train employees on security, and stay up to date on emerging threats.
Businesses incorporate reactive defense measures as well as preparatory measures. Reactively defending against cyber threats is like constantly putting out fires. Preparedness involves anticipating and proactively addressing potential security risks before they occur. By prioritizing preparedness, organizations can build robust defenses and respond more effectively to emerging threats. This enhances their overall cybersecurity posture. Being aware of predicted trends and how they could impact your organization is vital to developing a strong cybersecurity stance.
What are some trends anticipated in 2024?
1. Cybersecurity Skills Crunch
A significant cybersecurity skills shortage is highlighting the urgent need for more trained professionals. Businesses are recognizing the importance and value of investing in training, development, and upskilling programs as an avenue to strengthen and reinforce their defenses while mitigating risks.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
As AI technology evolves, AI attacks are getting more sophisticated. This includes deepfake social engineering attempts and automated malware that learns to avoid detection, making it harder for cybersecurity experts to keep up with these new threats.
AI can be used to assist in strengthening cybersecurity. AI is used for early detection making cyber incident responses more accurate. By quickly analyzing data and spotting abnormalities in real-time, AI helps organizations find and stop potential threats before they cause major damage.
3. Next Level Phishing
Advanced phishing, deep fake attacks, and AI-generated content are ushering in a new era of cyber deception. These tactics create convincing fake events that never happened, posing a big challenge for cybersecurity as they become more common.
4. Cybersecurity in the boardroom
Cybersecurity has transitioned from being solely an IT department concern to a top priority in the boardroom. More boards are recognizing the importance of including at least one member with expertise in cybersecurity to effectively address the evolving threat landscape and mitigate potential risks.
5. Focusing on both cyber resilience and cyber security
Cybersecurity primarily focuses on preventing cyber-attacks through various measures such as firewalls and antivirus software. Cyber resilience acknowledges that no system can guarantee 100% protection. Resilience emphasizes the ability to withstand and recover from attacks swiftly, ensuring continuity of operations even in the face of breaches or disruptions. Resiliency keeps operations going after an event, focusing on quick recovery with minimal data loss and downtime. Organizations can bounce back from disruptions and maintain essential functions, safeguarding their operations against potential cyber threats.
6. Less than Zero Trust
Less than zero trust means always verifying network activity, as there’s no safe perimeter. Security covers not just the corporate network but extends to remote workers, partner organizations, and IoT devices, recognizing that nothing should be trusted without confirmation.
7. Soft Skills
Soft skills are becoming increasingly necessary for cybersecurity professionals with the growing sophistication of cyber-attacks. Cyber professionals will need to weave together soft skills with technical expertise to strengthen the overall cybersecurity posture of their organization. Soft skills include communication, collaboration, and empathy.
8. Election year disinformation
During an election year, disinformation becomes a serious concern, with a rise in cyber-attacks anticipated to disrupt democratic processes. These attacks could target vital infrastructure like communications, public utilities, transportation, and security systems, aiming to create disorder and confusion in an attempt to wear down trust in the electoral system.
9. Cloud Attacks
Cloud attacks remain a major cybersecurity concern. Attackers are expected to use more advanced tactics in 2024. As businesses move more data and services to the cloud, attackers will likely focus on exploiting vulnerabilities. Organizations must enhance security measures to protect their data on multi-cloud setups.
10. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA is not a new trend, but will become increasingly popular in cybersecurity. As cyber threats evolve and increase, MFA will continue to prove important in the cyber protection of sensitive information. Organizations are expected to increase the adoption of MFA.
Who is responsible for developing a strategic plan to strengthen an organization’s cybersecurity stance?
In an organization, the leadership team is responsible for prioritizing cybersecurity and developing an environment that provides the proper scaffolding for the entire organization to be educated and prepared. The leadership team may include the CEO, CISO, and a Board of Directors, among others. In reality, cybersecurity is the responsibility of everyone in an organization. Everyone is at risk, regardless of role, length of employment, or previous background. Cybersecurity must be part of every organization’s culture.
Where do we find professional technical training in cybersecurity?
Professional technical training in cybersecurity can be found through a variety of platforms. These include online platforms and accredited higher education institutions offering education, certificates, and degrees in cybersecurity.
Organizations evaluate their needs and objectives, opting for either group or individualized training. Group sessions, whether in person or online, involve employees utilizing the same vendor/institution with a structured training path. Alternatively, individual training allows organizations to customize learning based on identified needs, goals, and each employee’s skillset.
In Montana, there are many pathways for professional technical training in cybersecurity. Cybersecurity training options include courses that align with the 52 NICCS work roles as outlined by the workforce framework for cybersecurity. The Cyber Rapid Training program provides entry-level and upskilling training in networking, operating systems, communication and cybersecurity. Both the training programs and the rapid training program provide support and scaffolding for individuals to test for and earn the CompTIA Network+ and Security+ Industry Recognized Credentials. Montana is privileged in being home to several Cybersecurity and IT certifications and degrees in most colleges and institutions statewide.
How do we move forward?
That is easy! Whether you are a CEO, CISO, board member, or employee, start the conversation on your organization’s needs, goals, and priorities. Once those are determined, find the right educational and training path for your community.

















![Everything You Need to Know About CyberMT’s GenCyber Camps [2023]](https://news.cyber.windfall.tools/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/CyberMT-blog-CTA-and-images-14.png.webp)

![Why Is Security Awareness Training Important? [2023]](https://news.cyber.windfall.tools/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/CyberMT-blog-CTA-and-images-13.png.webp)

![A Guide to Cybersecurity [2022]](https://news.cyber.windfall.tools/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/CyberMT-blog-CTA-and-images-10.png.webp)