Cybersecurity Awareness Month: Top 6 Cybersecurity Tips (2023)
October is National Cybersecurity Awareness Month. Held every year in October, the inaugural month of cybersecurity celebration began in 2004. The decision to focus on cybersecurity was a collaborative effort between the National Cyber Security Division within the Department of Homeland Security and the National Cyber Security Alliance (a nonprofit). The goal continues to be to ensure everyone has the resources needed to be as safe and secure online as possible. By putting a lens more directly on the importance of cybersecurity, the goal is to also provide both the public and private sectors with tools and resources to be proactive in enhancing cybersecurity practices. Intentional, strategic cybersecurity practices for both homes and businesses are the key to providing cyber vigilance.
What is the value of cybersecurity awareness?
Almost 90% of data breaches are caused by human error*; the human factor is the weakest link. Security-aware employees are one of the primary lines of defense in the business world. Security-aware family members are one of the primary lines of defense in your home. Security-aware individuals and organizations help provide protection from cyber threats, which are becoming stronger and increasingly relentless. By adding cyber security awareness to your toolbox, you better understand threats and how to prevent and/or abate cyber attacks.
What are the essential elements of good cybersecurity?
There are 6 main elements that should be addressed when considering cybersecurity:
- Application Security – Application security adds security measures inside the applications we all use every day. Examples are firewalls, antivirus software, and encryption techniques.
- Information Security – Information security references the security controls put into place to protect information collected by companies from their clients. Examples of the information to protect include personal data and login credentials.
- Network Security – Network security defends and protects computer networks from unauthorized network access.
- Operational Security – Security and risk management processes designed for risk management as countermeasures to reduce or eliminate threats to the exploitation of sensitive information.
- End-User Security – End-user security is educating your employees, and yourself, about cybersecurity best practices.
- Disaster Recovery Planning – Disaster recovery planning is your continuity plan describing the procedures and steps that are put in place to efficiently and successfully if a breach should occur.
How can we promote cybersecurity awareness?
The first step to promoting cybersecurity awareness is to lead by example. Make cybersecurity a priority in your life, at home, and at work. If you are an employer, take a look at what your current practices are, where you see room for improvement and assist your employees in increasing their cybersecurity awareness. If you are an employee, start the conversation with your employers about the importance of cybersecurity awareness and encourage them to look at their current practices as well as current best practices. Better yet, help them take these steps by working alongside them. The way to promote awareness is by making it a priority, not only for you but for those around you. We all continue to learn, and cyber threats and consistency continue to increase. Increasing awareness is for everyone, even those with background knowledge, experience and skills
Essential Cybersecurity Tips
Luckily, there are some key cybersecurity tips to assist in expanding your cybersecurity awareness.
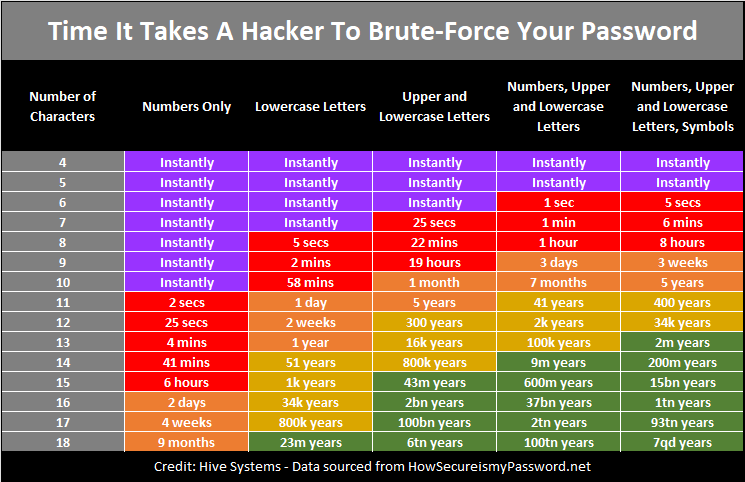
- Password Safety – Learning to construct a strong, unique password is critical.
TIP: Create strong, unique passwords. Create individual passwords for all accounts. See some key factors to a strong password here.
TIP: Use a password manager to keep track of your passwords. We know it is not a good idea to use the same password for all online accounts, let alone share a password with work and home log-ins. A password management application is safe, convenient, and assists with the lift of password management.
- Phishing – Knowing how to identify phishing and what to do if phishing is suspected can help protect your various accounts, and your identity, for both you and your employer.
TIP: Take a close look at your email before clicking any links. Keep an eye out for: spelling and grammar errors, things that sound too good to be true, nuances in the sender address that do not match the sender’s normal address, urgency, and requests for personal information.
TIP: Just as you clean your house regularly, regularly check to see if your email has been breached. Add this check to your routine, and always update passwords for accounts that have been breached. (Check if your email address was in a breach here.)
- Malware and Ransomware – Understanding the difference between these two words, what an attack can look like, and implementing prevention methods is a step towards limiting the impact these bring.
TIP: Hover over links to see and verify URLs before clicking. When in doubt, go directly to the source to verify requests or offers. Remember, “mail.google.com” is owned by Google, but “google.mail.com” is not.
- Mobile Device – Understanding how to keep data safe (application permissions, phone calls, network/Bluetooth connections, and sharing information between applications) protects you from threats you may not realize are there.
TIP: Don’t access workplace data on mobile devices unless authorized and necessary.
TIP: Use a VPN or your personal hotspot when on the move.
- Social Media – Implementing strong security settings and thoughtful consideration of what you share on social media helps keep you safe.
TIP: Use unique passwords for each social network and implement multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Work from Home – Recognizing the dangers of unknown networks, the importance of securing devices in transit and public places, and how to handle secure information helps you keep yourself and your organization safe while you work remotely.
TIP: Make sure all company data is saved on the company network, have a proper backup strategy, and follow all set cybersecurity policies of your employer.
What now?
The first step to increasing cybersecurity awareness is to start a conversation with those around you. Have a discussion as to why cybersecurity awareness is important, why you would like to focus on cybersecurity as a priority, and start building your plan to increase cybersecurity awareness.
There are a vast array of opportunities to take trainings or courses to add to your cybersecurity knowledge toolbox. Options include opportunities online and in person, short 20-30 minutes sessions to certification and degree opportunities. There are organizations out there that can help you determine goals, set up plans, and track progress for individuals and organizations as a whole. Assess your individual and organizational needs and determine what path is best for you and your team. What parameters fit your goals and needs.
Cybersecurity Awareness Can Be Fun!
Cybersecurity is of course about protection. Cybersecurity, and building your awareness can be fun as well! Check out cybersecurity awareness month activities in your area and see what events may be occurring. One example is Missoula College’s CyberSec Challenge occurring on October 28th. The event includes expert speakers from the cybersecurity field, challenges of increasing difficulty faced by teams of varying levels, and a prize to the winning team. It also includes enthusiastic participants who want to have some fun, test out their cybersecurity knowledge, or learn more about what a cyber threat may look like. We encourage you to look for events in your area and go have some cybersecurity awareness fun.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity-aware individuals are the primary line of defense from cyber threats and attacks. It is up to each of us to build up our toolbox. Our world continues to become interconnected at a rapid rate. It is up to you to become cyber-aware, but it takes all of us working together to protect the population at large. Working together to make cybersecurity awareness a priority, starting conversations, and taking action to learn more and make proactive plans and strategies will provide the strongest protection in a cyber-filled world.






